As we discussed earlier DBMS stands for Database Management System which helps us to work with the databases. This article is a part of a series on DBMS. To view the entire series, click here: https://binarybits.hashnode.dev/series/dbms
DBMS stands for Database Management System; it is the software used to work or manage databases. The main work of DBMS is to provide an interface for the user to manipulate data from the database.

DBMS acts as a middle layer between the user and the actual database. Users write logically structured queries or programs with the help of DBMS and the changes get reflected in the database and these changes occur due to the DBMS. You can refer to the following figure to visualize the work of DBMS.
CRUD Operations
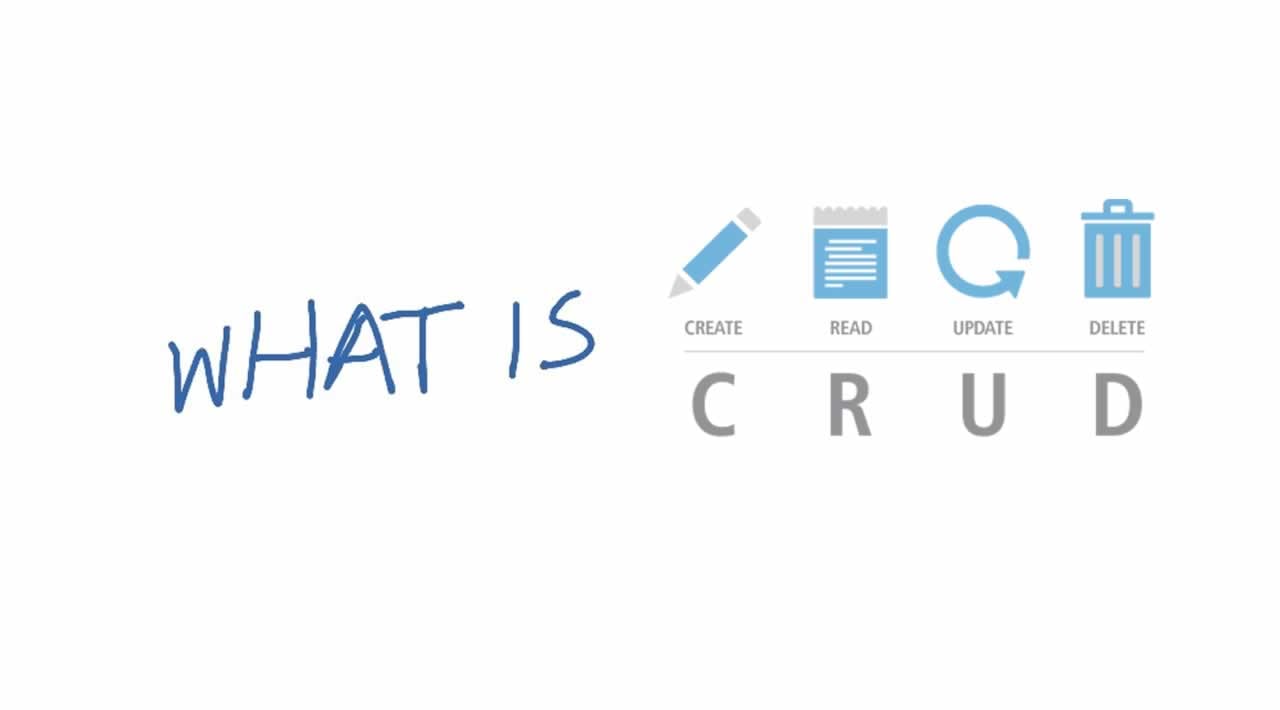
We use DBMS for so many things but one of the main uses is to perform the CRUD operations on the database. CRUD is an acronym that stands for –
C – Create
R – Read
U – Update
D – Delete
Let’s see CRUD in detail to understand what is DBMS and its actual work.
CREATE
Create means the creation of tables, rows, and columns with the help of DBMS. This is the operation where we insert the data and create other useful structures which help to efficiently work with the databases. When some users fill out the form on any website there are some queries written at the back end which performs the insert operation to store the user’s data.
READ
Read is an operation that is used so much in the DBMS. There is always a need to retrieve the data from the database. Whenever you see your friend’s image on Instagram it is retrieved from Instagram’s database. It is very important to retrieve the relevant information for the user whenever he uses an application.
UPDATE
The update operation is used to modify the existing data from the database. There is an always edit button on the social media apps which helps to update or modify the information in posts. Update operation needs to be performed with caution in DBMS so that we can update only those things which need to be changed and not others.
DELETE
Delete operation is simply used to delete the entry from the database. It needs to be used with extra caution so that useful information doesn’t get deleted.
Alongside CRUD DBMS is used for user administration as well. DBMS is used to register or monitor the users. DBMS helps to maintain data security, and data integrity and it also helps to monitor performance. Let us look at some characteristics of DBMS.
Characteristics of DBMS
There are various characteristics of Database management systems, these characteristics of DBMS make it useful for so many industrial and commercial business applications.
There are various characteristics of Database management systems, these characteristics of DBMS make it useful for so many industrial and commercial business applications.
1. Access security
Whenever someone wants to access the database he needs to be authenticated first. DBMS provides various security features so that unauthorized users can’t access the database.
2. Minimum data redundancy
Redundant data means duplicate or repeating data which increases the storage cost. DBMS also provides the feature to remove or minimize data redundancy with the help of normalization techniques.
3. Different views for different users
Different users need to be served with different data for eg. If the teacher logged in to an application he should be able to see the attendance of students and the results of all the students from his class. If a student logged in to the app then he would be able to see his result. So DBMS provides us the functionality to create different views of data for different users.
4. Multi-user environment for parallel data access
DBMS provides an ability to allow access for multiple users so that multiple users can access the data from the database. This functionality allows modern applications to handle a large user base.
5. Automatic backup and recovery
There are various functionalities provided by DBMS to ensure that data can’t get corrupted or lost in pandemic situations. There are options like rollback and commit which ensure that data can get recovered. Rollback is an operation to undo the changes and commit is the operation to make the changes permanent.
ACID Property of DBMS
It is one of the important properties of a database management system that makes sure the database always remains in a good state. Every operation which we perform on the database with the help of DBMS is known as a transaction and each of these transactions should follow the ACID property. ACID is an acronym that stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. It is one of the most important characteristics of DBMS.
ATOMICITY
The transaction never remains in between either it performs completely or gets discarded completely in the case of any system or DBMS failure.
CONSISTENCY
Data is very precious and it should remain the same before and after the transaction. It shouldn’t show any inconsistent behaviors with DBMS.
ISOLATION
All transactions should be isolated from one another, which means every transaction should be separate from one another there shouldn’t be any interference of one transaction onto another.
DURABILITY
After execution of the entire transaction, data should become permanent on the database. It should be durable i.e. it should remain there in case of system failure or system crash.
Archtitecture of DBMS
DBMS architecture describes the structure and how the users are connected to a specific database system. It also affects the performance of the database as it helps to design, develop, implement, and maintain the database management system. While planning any structure, the architects design and develop the organization and the layout of the individual components used to build the whole structure and their relationships. This determines the structural integrity and durability of the entire complex, i.e., the architecture defines the structure's performance.
This concept is also true in the case of the database management system. The DBMS architecture affects the performance of the database as it helps to design, develop, implement, and maintain the database management system. The database management system design depends on the DBMS architecture for its representation. It describes the structure and how the users are connected to a specific database system.
Database management systems are divided into multiple levels of abstraction for proper functioning. These modules/layers describe the functioning and the design of the DBMS.
Since a database management system is not always directly accessible by the user or an application, we can maintain it with the help of various architectures based on how the user is connected to the database. These architectures follow a tier-based classification, i.e., the DBMS architecture is classified depending on how many layers are present in the structure of the DBMS.
Hence, an n-tier DBMS Architecture divides the whole DBMS into related but n-independent layers or levels, i.e., a one-tier architecture divides the DBMS into a single layer, a two-tier DBMS architecture divides the DBMS into two layers, a three-tier in three layers, and so on. When the layers are increased in the architecture, the level of abstraction also increases, increasing the security and complexity of the DBMS structure. All these layers are independent, i.e., any modification performed in a particular layer does not affect the other layer present in the architecture.
Now, let’s look at the most common DBMS architectures:
Single Tier Architecture or One-Tier Architecture
Two-Tier Architecture
Three-Tier Architecture
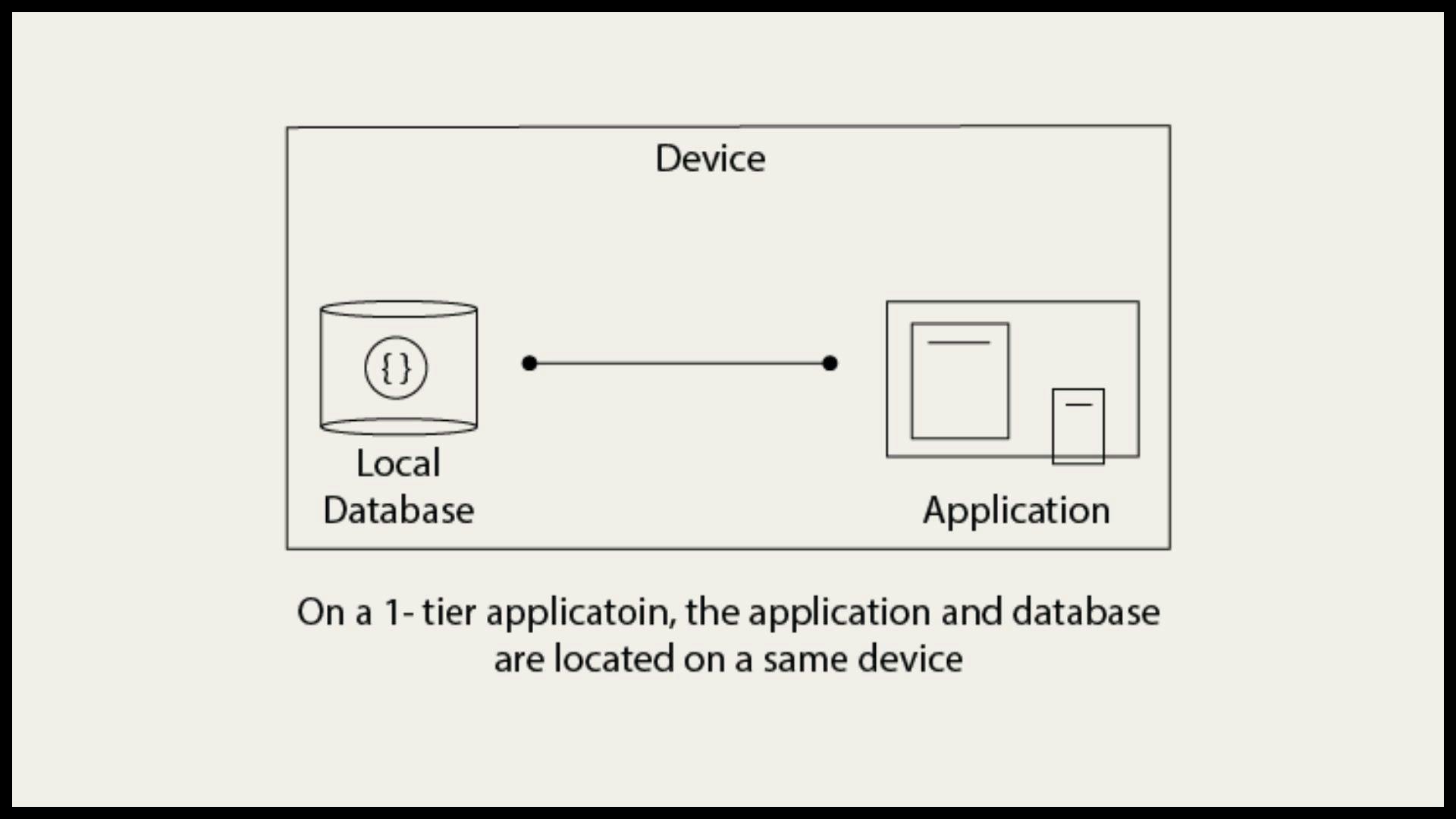
SINGLE TIER ARCHITECTURE
In this architecture, the database is directly available to the user. It means the user can directly sit on the DBMS and uses it. Any changes done here will directly be done on the database itself. It doesn't provide a handy tool for end users. The 1-Tier architecture is used for the development of the local application, where programmers can directly communicate with the database for quick response.
Single Tier DBMS Architecture is used whenever:
The data isn't changed frequently.
No multiple users are accessing the database system.
We need a direct and simple way to modify or access the database for application development.
Let us take an example of Single Tier Architecture. To learn the Structure Query Language (SQL), we set up our SQL server and the database on our local system. This SQL server enables us to directly interact with the relational database and execute certain operations without requiring any network connection. This whole setup to learn SQL queries is an example of Single-Tier DBMS architecture.
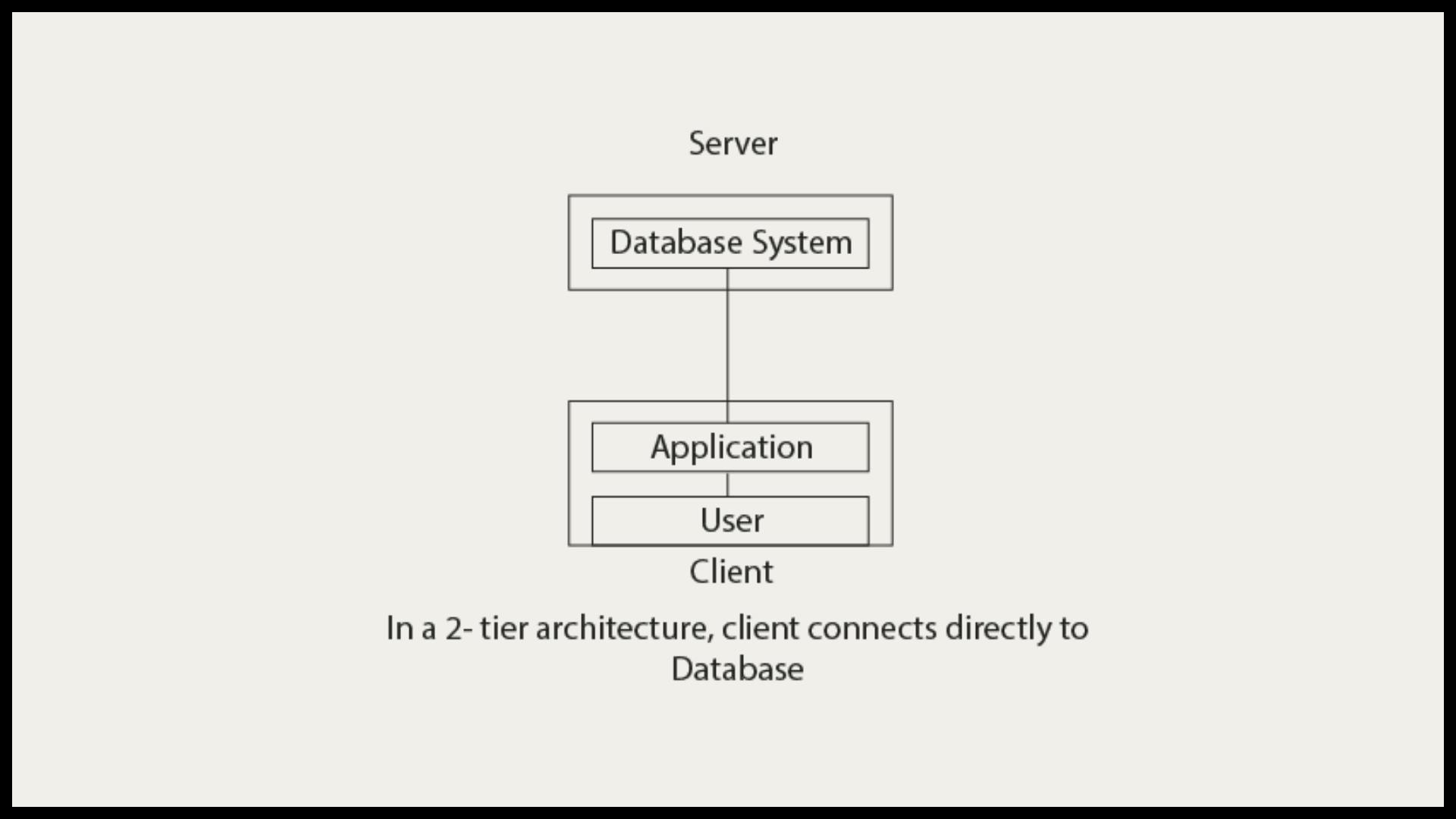
TWO TIER ARCHITECTURE
The 2-Tier architecture is the same as the basic client-server. In the two-tier architecture, applications on the client end can directly communicate with the database on the server side. For this interaction, APIs like ODBC, and JDBC are used. The user interfaces and application programs are run on the client side. The server side is responsible to provide the functionalities like query processing and transaction management. To communicate with the DBMS, the client-side application establishes a connection with the server side.
The main advantages of having a two-tier architecture over a single-tier are:
Multiple users can use it at the same time. Hence, it can be used in an organization.
It has high processing ability as the database functionality is handled by the server alone.
Faster access to the database due to the direct connection and improved performance.
Because of the two independent layers, it's easier to maintain.
The main disadvantages of Two-Tier DBMS Architecture are:
Scalability - As the number of clients increases, the load on the server increases. Thereby declining the performance of the DBMS and, in turn, the client-side application.
Security - The Direct connection between the client and server systems makes this architecture vulnerable to attacks.
Let us take an example of two-tier architecture. Consider a situation where you went to a bank to withdraw some cash. After entering the withdrawal amount and the account details on the withdrawal slip, the banker will go through the server-side database via his credential (API call) and will check whether there is enough balance present or not. This client-server model is an example of a Two-Tier DBMS architecture.
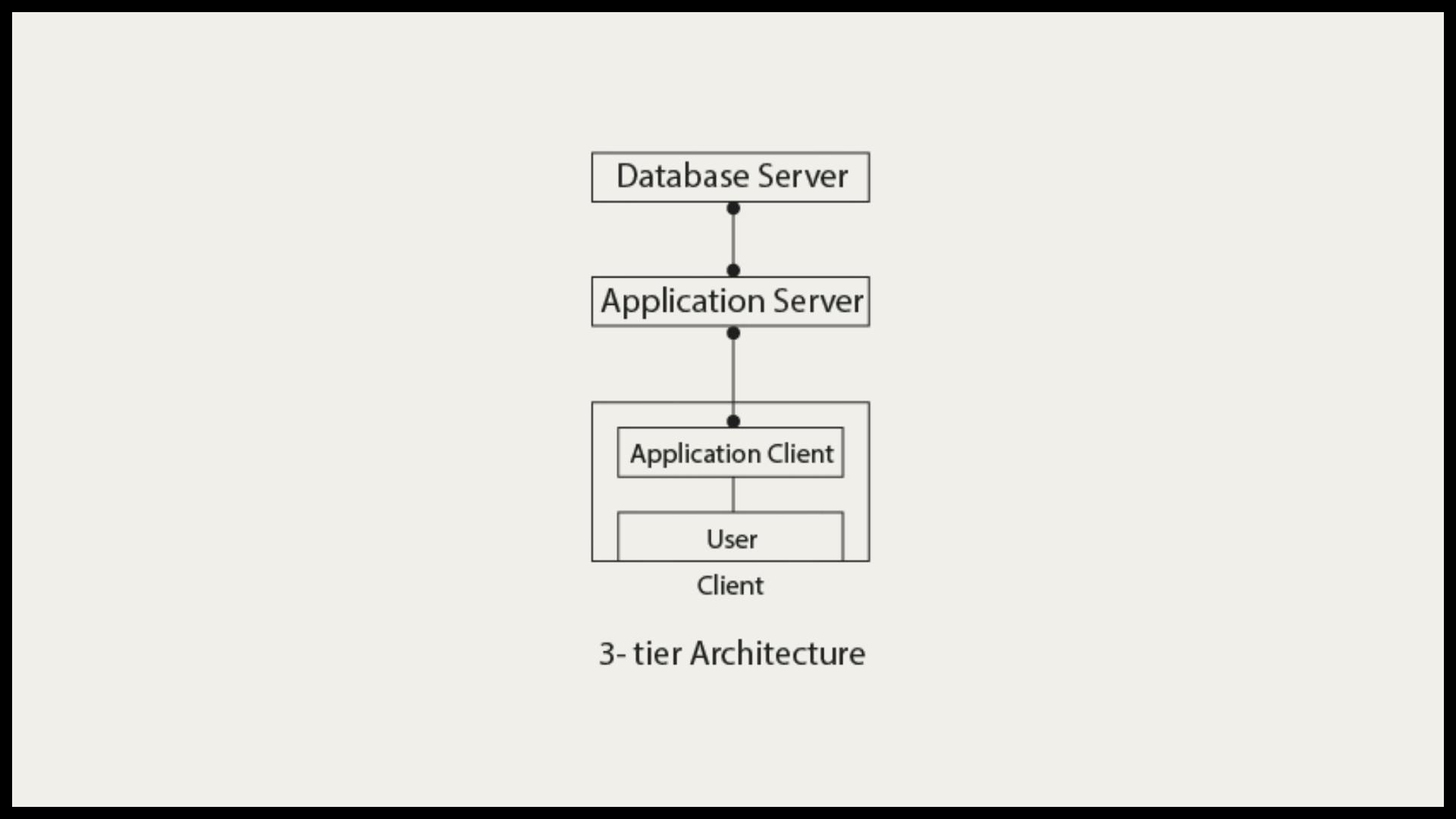
THREE TIER ARCHITECTURE
The 3-Tier architecture contains another layer between the client and server. In this architecture, the client can't directly communicate with the server. The application on the client end interacts with an application server which further communicates with the database system. The end-user has no idea about the existence of the database beyond the application server. The database also has no idea about any other user beyond the application. The 3-Tier architecture is used in the case of the large web application.
The main advantages of Three Tier DBMS Architecture are:
Scalability - Since the database server isn't aware of any users beyond the application layer and the application layer implements load balancing, there can be as many clients as you want.
Data Integrity - Data corruption and bad requests can be avoided because of the checks performed in the application layer on each client request.
Security - The removal of the direct connection between the client and server systems via abstraction reduces unauthorized access to the database.
In Three Tier DBMS Architecture, an additional layer (Application Layer) is added between the Client and the Server. This increases the number of layers present between the DBMS and the end-users, making the implementation of the DBMS structure complex and difficult to maintain.
In summary, 3-tier architecture is more flexible, scalable, and secure than 2-tier architecture, but it is also more complex and requires more maintenance. The choice between 2-tier and 3-tier architecture depends on the specific requirements of the project.
